TLS certificate
Description: TLS certificate
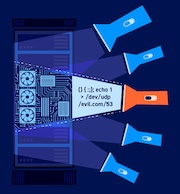
TLS (or SSL) helps to protect the confidentiality and integrity of information in transit between the browser and server, and to provide authentication of the server's identity. To serve this purpose, the server must present an TLS certificate that is valid for the server's hostname, is issued by a trusted authority and is valid for the current date. If any one of these requirements is not met, TLS connections to the server will not provide the full protection for which TLS is designed.
It should be noted that various attacks exist against TLS in general, and in the context of HTTPS web connections in particular. It may be possible for a determined and suitably-positioned attacker to compromise TLS connections without user detection even when a valid TLS certificate is used.
References
Vulnerability classifications
- CWE-295: Improper Certificate Validation
- CWE-326: Inadequate Encryption Strength
- CWE-327: Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm
Typical severity
Medium
Type index (hex)
0x01000100
Type index (decimal)
16777472